Docker 1.12 introduced Services. A replicated, distributed and load balanced service can be easily created using docker service create command. A “desired state” of the application, such as run 3 containers of Couchbase, is provided and the self-healing Docker engine ensures that that many containers are running in the cluster. If a container goes down, another container is started. If a node goes down, containers on that node are started on a different node.
This blog will show how to setup a Couchbase cluster using Docker Services.
Many thanks to @marcosnils, another fellow Docker Captain, to help me debug the networking!
Couchbase Cluster
A cluster of Couchbase Servers is typically deployed on commodity servers. Couchbase Server has a peer-to-peer topology where all the nodes are equal and communicate to each other on demand. There is no concept of master nodes, slave nodes, config nodes, name nodes, head nodes, etc, and all the software loaded on each node is identical. It allows the nodes to be added or removed without considering their “type”. This model works particularly well with cloud infrastructure in general.
- Start Couchbase: Start n Couchbase servers
- Create cluster: Pick any server, and add all other servers to it to create the cluster
- Rebalance cluster: Rebalance the cluster so that data is distributed across the cluster
Setup Swarm Mode on Ubuntu
- Launch an Ubuntu instance on Amazon. This blog used
mx4.largesize for the AMI. - Install Docker:
123curl -sSL https://get.docker.com/ | sh - Docker Swarm mode is an optional feature and need to be explicitly enabled. Initialize Swarm mode:
123docker swarm init
Create Couchbase “master” Service
- Create an overlay network:
This is required so that multiple Couchbase Docker containers in the cluster can talk to each other.123docker network create -d overlay couchbase - Create a “master” service:
123docker service create --name couchbase-master -p 8091:8091 --replicas 1 --network couchbase -e TYPE=MASTER arungupta/couchbase:swarmThis image is created using the Dockerfile here. This Dockerfile uses a configuration script to configure the base Couchbase Docker image. First, it uses Couchbase REST API to setup memory quota, setup index, data and query services, security credentials, and loads a sample data bucket. Then, it invokes the appropriate Couchbase CLI commands to add the Couchbase node to the cluster or add the node and rebalance the cluster. This is based upon three environment variables:TYPE: Defines whether the joining pod is worker or masterCOUCHBASE_MASTER: Name of the master serviceAUTO_REBALANCE: Defines whether the cluster needs to be rebalanced
For this first configuration file, the TYPE environment variable is set to MASTER and so no additional configuration is done on the Couchbase image.This service also uses the previously created overlay network named
couchbase. It exposes the port 8091 that makes the Couchbase Web Console accessible outside the cluster. This service contains only one replica of the container. - Check status of the Docker service:
12345ubuntu@ip-172-31-26-234:~$ docker service lsID NAME REPLICAS IMAGE COMMANDcecl1rl5ecyr couchbase-master 1/1 arungupta/couchbase:swarm
It shows that the service is running. The “desired” and “expected” number of replicas are 1, and thus are matching.
- Check the tasks in the service:
12345ubuntu@ip-172-31-26-234:~$ docker service ps couchbase-masterID NAME IMAGE NODE DESIRED STATE CURRENT STATE ERROR2xuw1h0jvantsgj9f8zuj03k8 couchbase-master.1 arungupta/couchbase:swarm ip-172-31-26-234 Running Running 30 seconds ago
This shows that the container is running.
- Access Couchbase Web Console using public IP address and it should look like:
The image used in the configuration file is configured with theAdministratorusername andpasswordpassword. Enter the credentials to see the console:
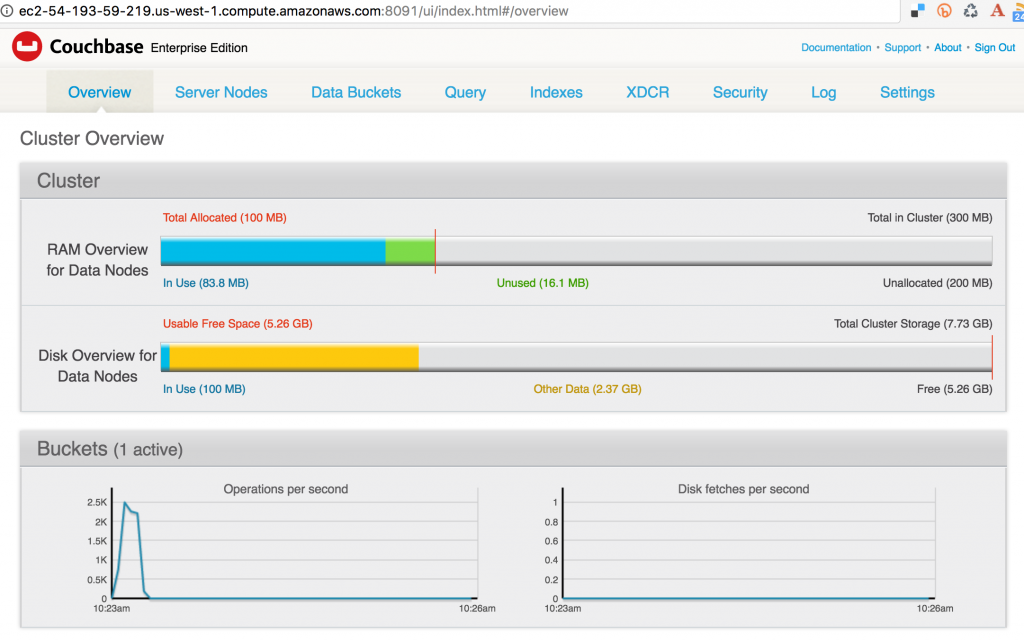
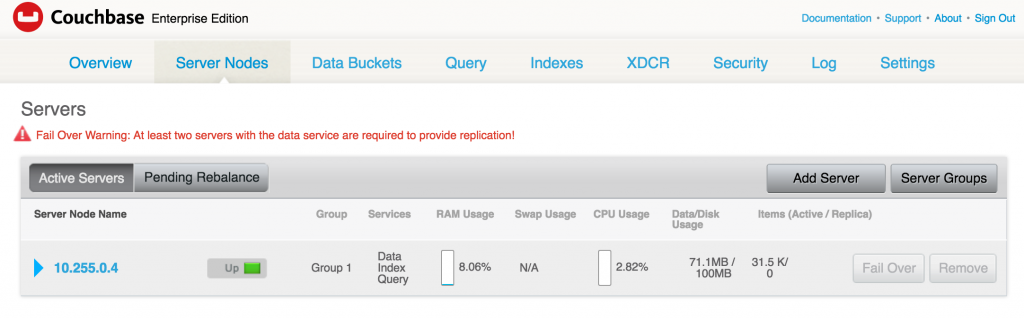
- Click on Server Nodes to see how many Couchbase nodes are part of the cluster. As expected, it shows only one node:
Create Couchbase “worker” Service
- Create “worker” service:
123docker service create --name couchbase-worker --replicas 1 -e TYPE=WORKER -e COUCHBASE_MASTER=couchbase-master.couchbase --network couchbase arungupta/couchbase:swarm
This RC also creates a single replica of Couchbase using the same
arungupta/couchbase:swarmimage. The key differences here are:TYPEenvironment variable is set toWORKER. This adds a worker Couchbase node to be added to the cluster.COUCHBASE_MASTERenvironment variable is passed the name of the master service,couchbase-master.couchbasein our case. This uses the service discovery mechanism built into Docker for the worker and the master to communicate.
- Check service:
123456ubuntu@ip-172-31-26-234:~$ docker service lsID NAME REPLICAS IMAGE COMMANDaw22g79o3u8z couchbase-worker 1/1 arungupta/couchbase:swarmcecl1rl5ecyr couchbase-master 1/1 arungupta/couchbase:swarm - Checking the Couchbase Web Console shows the updated output:
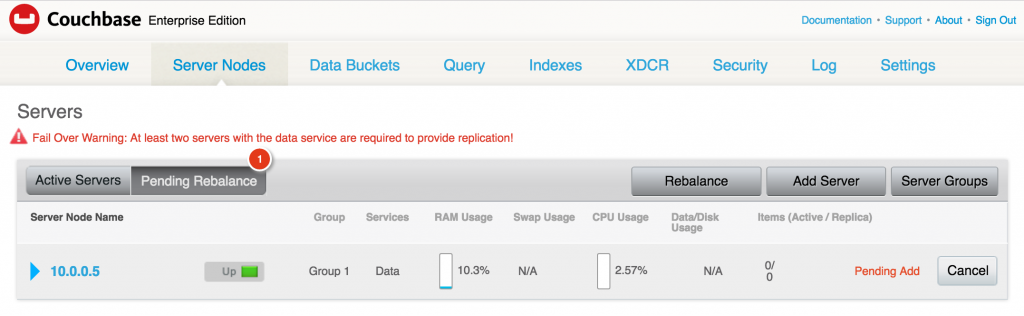
It shows that one server is pending to be rebalanced.During the worker service creation,AUTO_REBALANCEenvironment variable could have been set totrueorfalseto enable rebalance. This ensures that the node is only added to the cluster but the cluster itself is not rebalanced. Rebalancing the cluster requires to re-distribute the data across multiple nodes of the cluster. The recommended way is to add multiple nodes, and then manually rebalance the cluster using the Web Console.
Add Couchbase Nodes by Scaling Docker Service
- Scale the service:
123docker service scale couchbase-worker=2 - Check the service:
This shows that 2 replicas of worker are running.123456ubuntu@ip-172-31-20-209:~$ docker service lsID NAME REPLICAS IMAGE COMMAND1k650zjrwz00 couchbase-master 1/1 arungupta/couchbase:swarm5o1i4eckr9d3 couchbase-worker 2/2 arungupta/couchbase:swarm - Check the Couchbase Web Console:
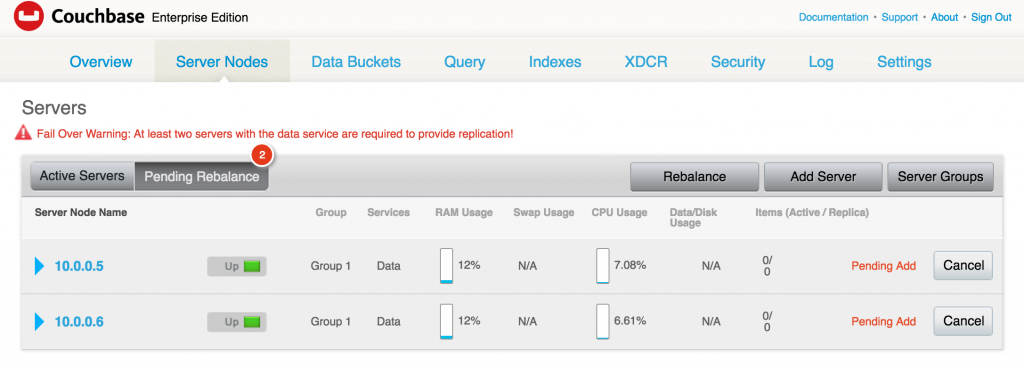 As expected, two servers are now added in the cluster and pending rebalance.
As expected, two servers are now added in the cluster and pending rebalance.
- Optionally, you can rebalance the cluster by clicking on the
Rebalancebutton. and it will show like: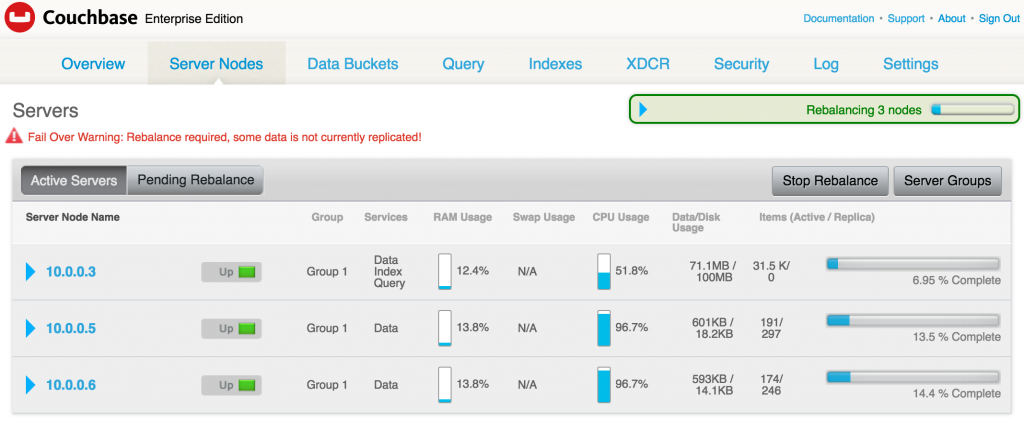 After the rebalancing is complete, the Couchbase Web Console is updated to as as shown:
After the rebalancing is complete, the Couchbase Web Console is updated to as as shown:
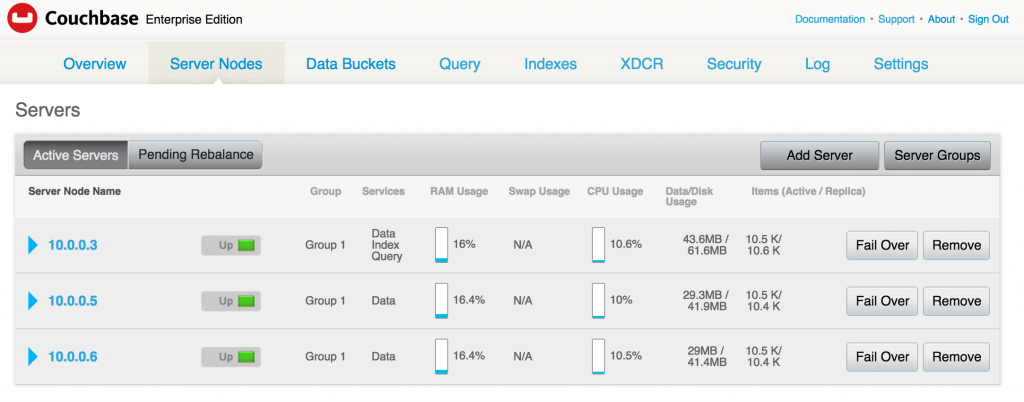
- See all the running containers using
docker ps:
1234567ubuntu@ip-172-31-26-234:~$ docker psCONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMESa0d927f4a407 arungupta/couchbase:swarm "/entrypoint.sh /opt/" 21 seconds ago Up 20 seconds 8091-8094/tcp, 11207/tcp, 11210-11211/tcp, 18091-18093/tcp couchbase-worker.2.4ufdw5rbdcu87whgm94yfv9yk22bde7f6471c arungupta/couchbase:swarm "/entrypoint.sh /opt/" 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes 8091-8094/tcp, 11207/tcp, 11210-11211/tcp, 18091-18093/tcp couchbase-worker.1.f22c2gghu88bnbjl5ko1wlru5f97e8bc091c3 arungupta/couchbase:swarm "/entrypoint.sh /opt/" 7 minutes ago Up 7 minutes 8091-8094/tcp, 11207/tcp, 11210-11211/tcp, 18091-18093/tcp couchbase-master.1.2xuw1h0jvantsgj9f8zuj03k8
In addition to creating a cluster, Couchbase Server supports a range of high availability and disaster recovery (HA/DR) strategies. Most HA/DR strategies rely on a multi-pronged approach of maximizing availability, increasing redundancy within and across data centers, and performing regular backups.
Now that your Couchbase cluster is ready, you can run your first sample application.
Learn more about Couchbase and Containers:
- Couchbase on Containers
- Follow us on @couchbasedev or @couchbase
- Ask questions on Couchbase Forums
Source: http://blog.couchbase.com/2016/september/docker-service-swarm-mode-couchbase-cluster




Every peoples connected the internet and searching many websites daily and also types data, how to delete browsing history information’s even passwords all are save into the browsing history so it will keep save in your privacy then this website is useful for you.
From this one might conclude that Perception is a few styles of a trick that helps the USA to require these spectral pictures and turns them into a world we are able to associate and act with. assignment writing service – assignmentdoer.com. This clever device looks to be a creation of our intellect that allows the USA to act with one another in what seems to be a 3-dimensional reality.
It shows that one server is pending to be rebalanced.During the worker service creation, AUTO_REBALANCE environment variable could have been set to true or false to enable rebalance. This ensures that the node is only added to the cluster but the cluster itself is not rebalanced. Rebalancing the cluster requires to re-distribute the data across multiple nodes of the cluster. The recommended way is to add multiple nodes, and then manually rebalance the cluster using the Web Console.
This is also a very good post which I really enjoyed reading. It is not everyday that I have the possibility to see something like this.