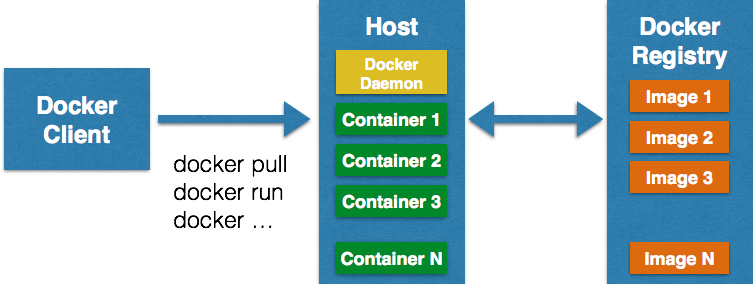
Running Docker containers typically involve three components:
- Docker Client is a binary that accepts commands from the user and communicates back and forth with host
- Docker Daemon runs on a host machine and does the heavy lifting of building, running, and distributing Docker containers
- Docker Registry is SaaS platform for sharing and managing Docker images.Docker Hub is a public hub. Private registries can be easily setup as well, such as one by Artifactory. More on this in a subsequent blog.
Docker Client communicates with Daemon, either co-located on the same host, or on a different host. It requests the Daemon to pull an image from the repository using pull command. The Daemon then downloads the image from Docker Hub, or whatever registry is configured. Multiple images can be downloaded from the registry and installed on Daemon host.
In a typical development environment setup, Docker Client and Host/Daemon will be co-located on the same host machine. Even if they are on separate machines, it still require to login to the Host and setup Docker Daemon for that OS.
 Docker Machine takes you from zero-to-Docker on a host with a single command. This host could be your laptop, in the cloud, or in your data center. It creates servers, installs Docker on them, then configures the Docker client to talk to them.
Docker Machine takes you from zero-to-Docker on a host with a single command. This host could be your laptop, in the cloud, or in your data center. It creates servers, installs Docker on them, then configures the Docker client to talk to them.
This downloads the boot2docker VM, setup ssh keys, generate certificates, start the VM. It basically takes care of all the boring work so that you can focus on all the fun things.
This Tech Tip will show you to get started with Docker Machine and use it to setup Docker Host on Mac. It does not work on Windows yet because of github.com/docker/machine/issues/742.
Lets get started!
Install Docker Machine
- Download the appropriate binary from docs.docker.com/machine/#installation. Binary for Mac can be downloaded as:
12345678~> curl -L https://github.com/docker/machine/releases/download/v0.1.0/docker-machine_darwin-amd64 > /usr/local/bin/docker-machine% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time CurrentDload Upload Total Spent Left Speed100 403 0 403 0 0 725 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 726100 15.5M 100 15.5M 0 0 2276k 0 0:00:06 0:00:06 --:--:-- 3362k~> chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-machine - Verify the installation as:
1234~> docker-machine -vdocker-machine version 0.1.0
Setup Mac Host using Docker Machine
- Docker Machine can be configured to use with multiple drivers, such as Amazon Web Services, Google Compute Engine, Microsoft Azure, and Oracle VirtualBox. On a developer laptop, Virtual Box is a convenient option.Virtual Box 4.3.20 is the minimum requirement. So make sure you’ve the correct version installed.
- Create a Docker Host using VirtualBox provider and call the machine as “mydocker”.Make sure ssh-keygen is in the PATH before invoking this command. On Mac, this is already in /usr/bin/ssh-keygen. On Windows, this can be installed as part of Git Bash.This can be done as:
This downloads boot2docker with the Docker daemon installed, and will create and start a VirtualBox VM with Docker running.123456789101112~> docker-machine create --driver virtualbox mydockerINFO[0000] Creating CA: /Users/arungupta/.docker/machine/certs/ca.pemINFO[0000] Creating client certificate: /Users/arungupta/.docker/machine/certs/cert.pemINFO[0002] Downloading boot2docker.iso to /Users/arungupta/.docker/machine/cache/boot2docker.iso...INFO[0006] Creating SSH key...INFO[0007] Creating VirtualBox VM...INFO[0018] Starting VirtualBox VM...INFO[0018] Waiting for VM to start...INFO[0051] "mydocker" has been created and is now the active machine.INFO[0051] To point your Docker client at it, run this in your shell: $(docker-machine env mydocker) - Find IP address of the machine as:
Note down this IP address, this will be used for accessing the application.1234~> docker-machine ip192.168.99.101 - Check the status of running machine as:
The12345~> docker-machine lsNAME ACTIVE DRIVER STATE URL SWARMmydocker * virtualbox Running tcp://192.168.99.101:2376*in theACTIVEcolumn indicates this is an active host. - Check the environment of newly created machine as:
123456~> docker-machine env mydockerexport DOCKER_TLS_VERIFY=yesexport DOCKER_CERT_PATH=/Users/arungupta/.docker/machine/machines/mydockerexport DOCKER_HOST=tcp://192.168.99.101:2376
Setup Docker client to Communicate
- Setup your client to talk to this host as:
123$(docker-machine env mydocker)
Run Java Application on Host
- Run Java EE 7 Application discussed in Java EE 7 Hands-on Lab on WildFly and Docker on this host as:
123456789101112131415161718docker run -it -p 8080:8080 arungupta/javaee7-holUnable to find image 'arungupta/javaee7-hol' locallyPulling repository arungupta/javaee7-hola068decaf892: Download complete511136ea3c5a: Download complete5b12ef8fd570: Download completeae0c2d0bdc10: Download complete. . .03:13:20,449 INFO [org.jboss.resteasy.spi.ResteasyDeployment] (MSC service thread 1-12) Adding provider class org.javaee7.movieplex7.json.MovieReader from Application class org.javaee7.movieplex7.rest.ApplicationConfig03:13:20,554 INFO [org.wildfly.extension.undertow] (MSC service thread 1-12) JBAS017534: Registered web context: /movieplex703:13:20,596 INFO [org.jboss.as.server] (ServerService Thread Pool -- 31) JBAS018559: Deployed "movieplex7-1.0-SNAPSHOT.war" (runtime-name : "movieplex7-1.0-SNAPSHOT.war")03:13:20,674 INFO [org.jboss.as] (Controller Boot Thread) JBAS015961: Http management interface listening on http://127.0.0.1:9990/management03:13:20,675 INFO [org.jboss.as] (Controller Boot Thread) JBAS015951: Admin console listening on http://127.0.0.1:999003:13:20,675 INFO [org.jboss.as] (Controller Boot Thread) JBAS015874: WildFly 8.2.0.Final "Tweek" started in 10513ms - Started 400 of 452 services (104 services are lazy, passive or on-demand) - Access the application at 192.168.99.101:8080/movieplex7/ and looks like:

Docker Machine Commands
Complete list of Docker Machine commands can be seen as:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
~> docker-machine
NAME:
docker-machine - Create and manage machines running Docker.
USAGE:
docker-machine [global options] command [command options] [arguments...]
VERSION:
0.1.0
AUTHOR:
Docker Machine Contributors - <https://github.com/docker/machine>
COMMANDS:
active Get or set the active machine
create Create a machine
config Print the connection config for machine
inspect Inspect information about a machine
ip Get the IP address of a machine
kill Kill a machine
ls List machines
restart Restart a machine
rm Remove a machine
env Display the commands to set up the environment for the Docker client
ssh Log into or run a command on a machine with SSH
start Start a machine
stop Stop a machine
upgrade Upgrade a machine to the latest version of Docker
url Get the URL of a machine
help, h Shows a list of commands or help for one command
GLOBAL OPTIONS:
--debug, -D Enable debug mode
--storage-path "/Users/arungupta/.docker/machine" Configures storage path [$MACHINE_STORAGE_PATH]
--tls-ca-cert "/Users/arungupta/.docker/machine/certs/ca.pem" CA to verify remotes against [$MACHINE_TLS_CA_CERT]
--tls-ca-key "/Users/arungupta/.docker/machine/certs/ca-key.pem" Private key to generate certificates [$MACHINE_TLS_CA_KEY]
--tls-client-cert "/Users/arungupta/.docker/machine/certs/cert.pem" Client cert to use for TLS [$MACHINE_TLS_CLIENT_CERT]
--tls-client-key "/Users/arungupta/.docker/machine/certs/key.pem" Private key used in client TLS auth [$MACHINE_TLS_CLIENT_KEY]
--help, -h show help
--version, -v print the version
|
Learn more about Docker Machine, Swarm, and Compose in this video:
Why would you use anything else other than Docker Machine to setup Docker host? How do you setup Docker Host otherwise?
Some useful references …
- Full documentation
- GitHub Repo
- Issues
- #docker-machine on freenode
Enjoy!



11 thoughts on “Docker Machine to Setup Docker Host – Tech Tip #78”